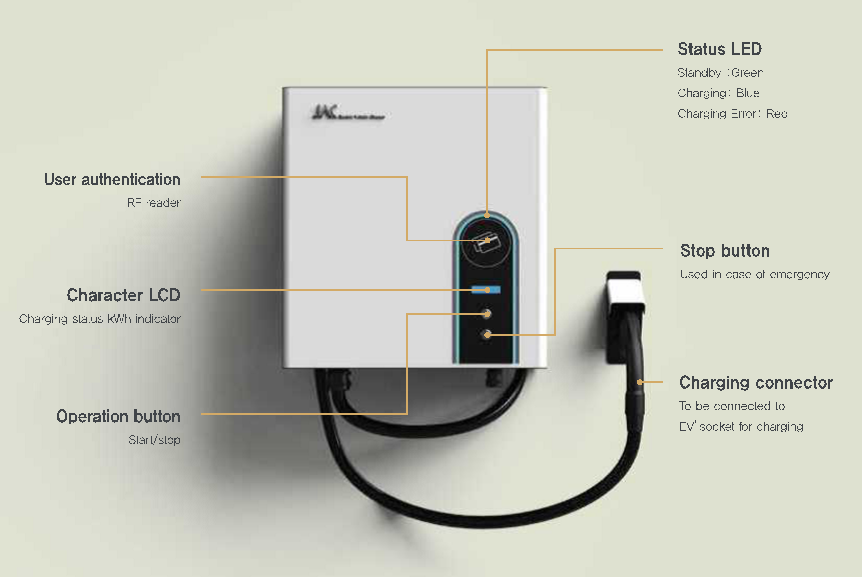
EV Chargers

Evs have approx. 90% fewer moving parts than an ICE(internal combustion engine) vehicle.
Here are the key components of an EV;
- Electric Engine/Motor- Provides power to rotate the wheels. It can be DC/AC type.
- Inverter- Converts the electric current in the form of Direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC) for the vehicle’s motor if required.
- Drivetrain- EVs have a single-speed transmission which send power from the motor to the all the wheels.
- Batteries- Store the electricity required to run an EV. The higher the kW of the battery, the higher the driving range.
- Charging Port- plug into an outlet or EV charging point to charge your battery.
How are EVs charged ?
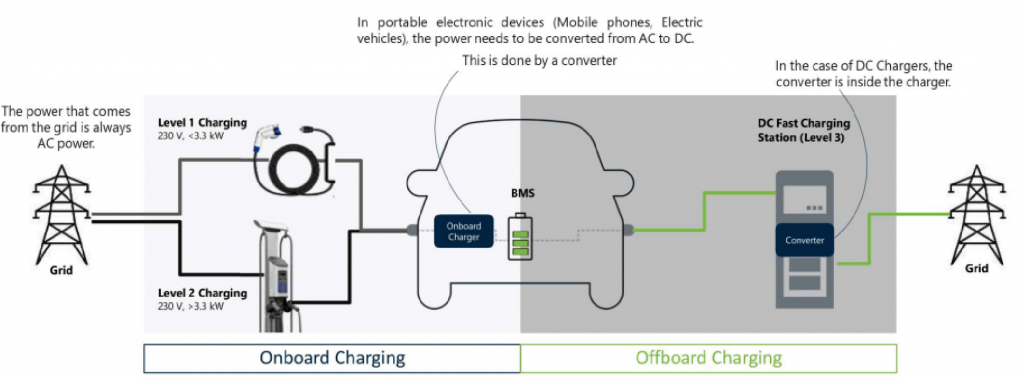
L1 vs L2 vs L3: Level of charging
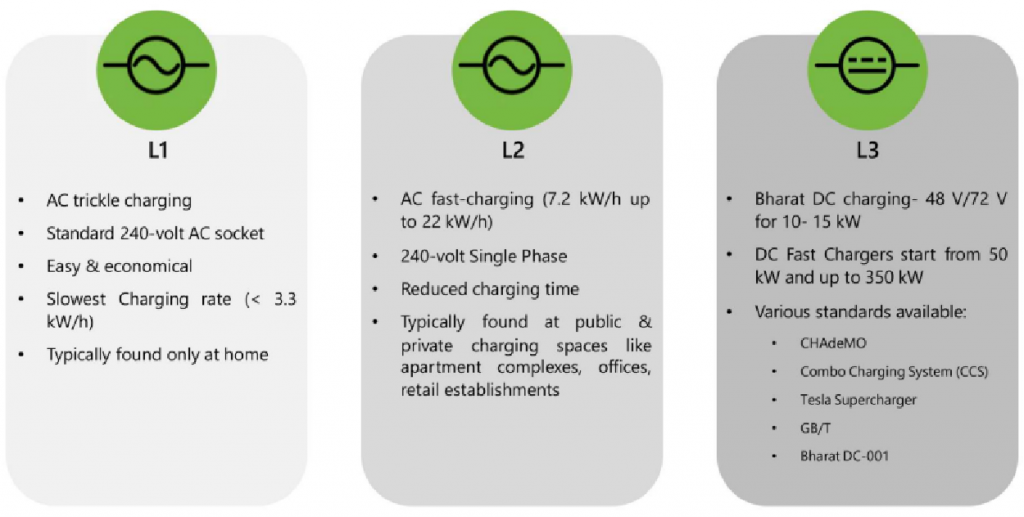
Where the AC Charging makes sense?

Where the DC charging makes sense?

DC chargers are mainly used for 4 wheelers that have very high utilization. These would includes scenarios, where
- You operate a commercial fleet and need fast charging to enhance your vehicle utilization.
- Heavy Vehicles –Cargos, Trucks which have large batteries and travels long distance-need access to fast charging.
- Highway fast chargers are required to support long distance Electrick vehicles.
- You are running a charge point network and need to install DC chargers as part of the Govt. mandate.
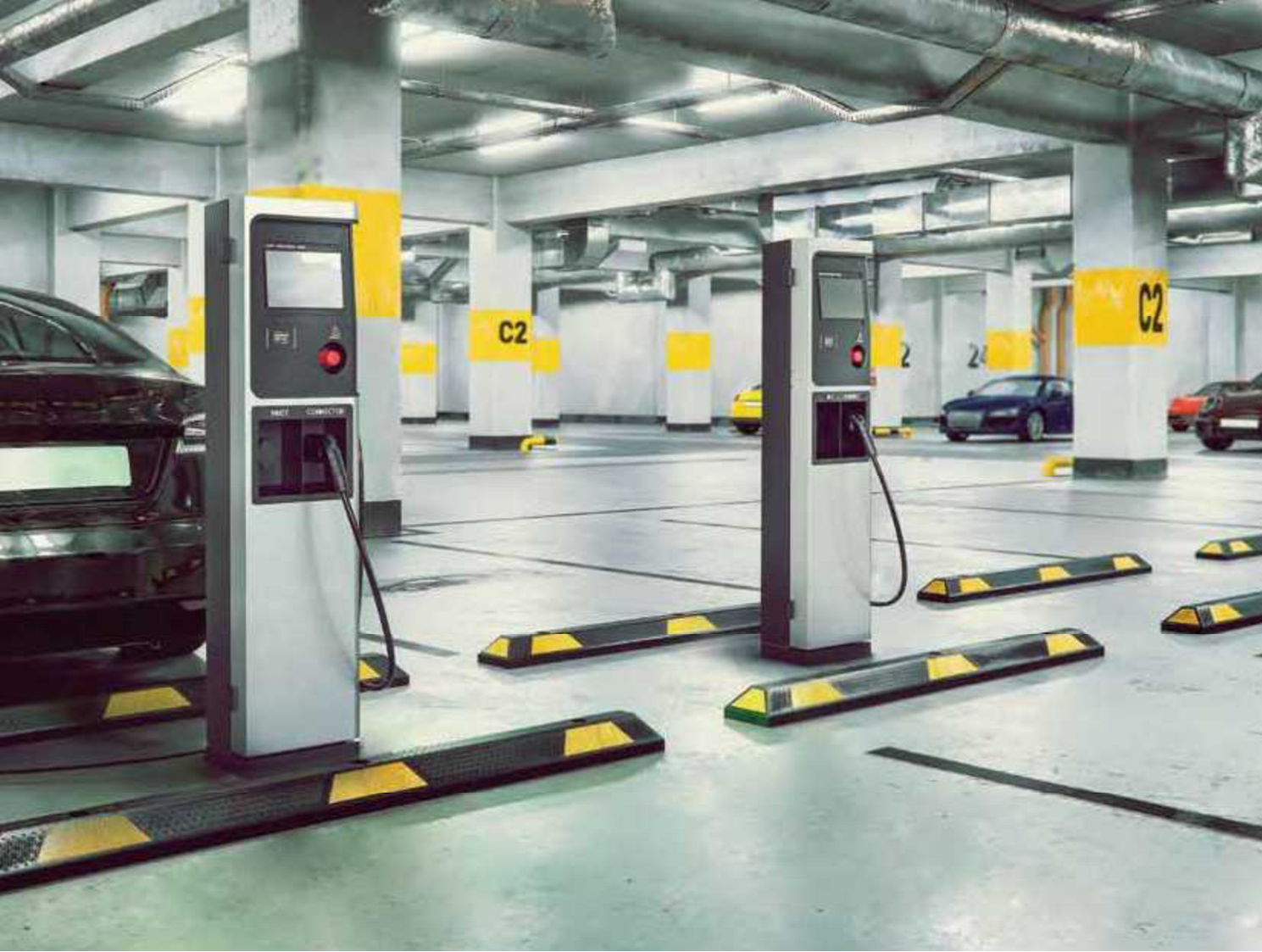
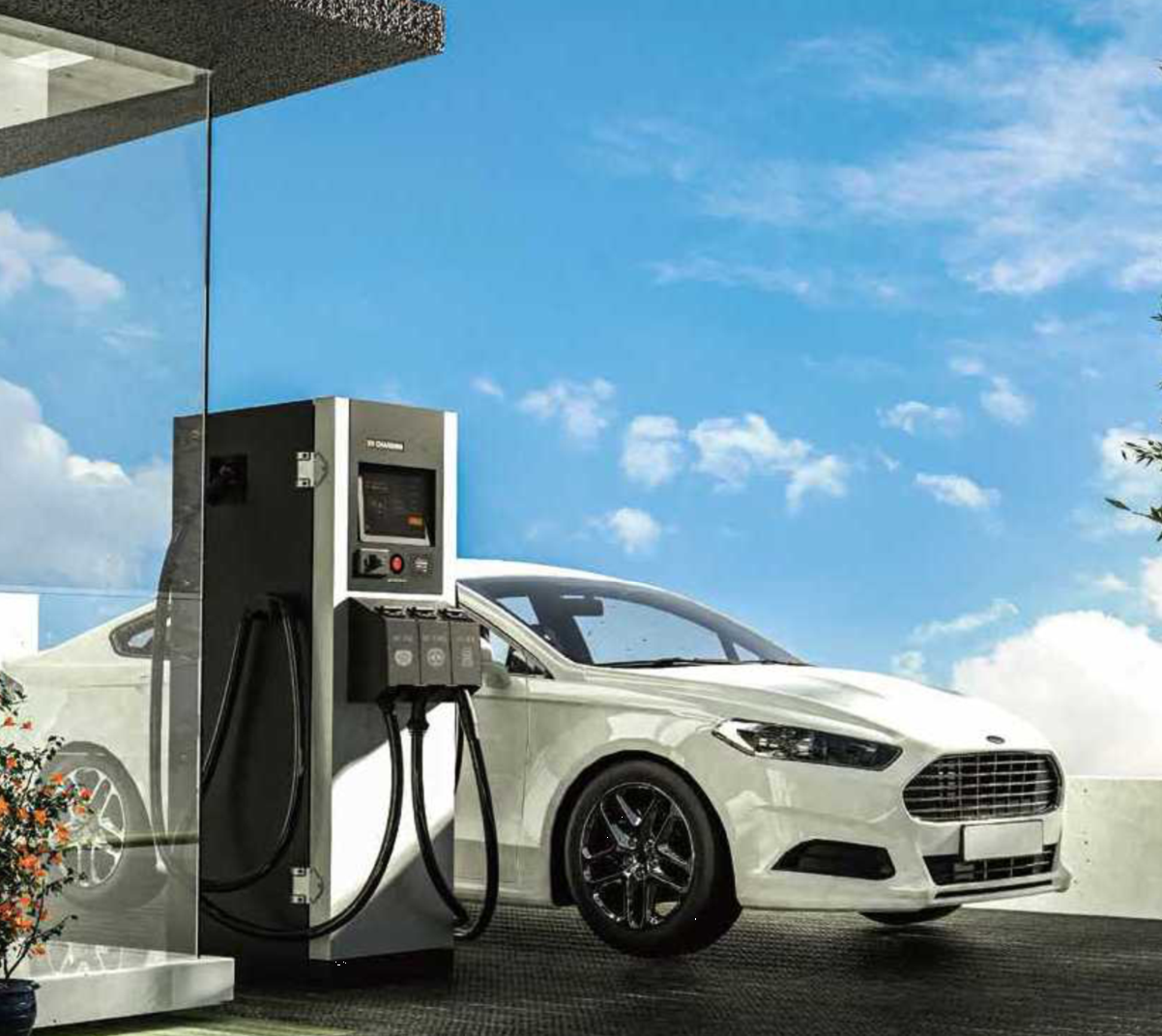
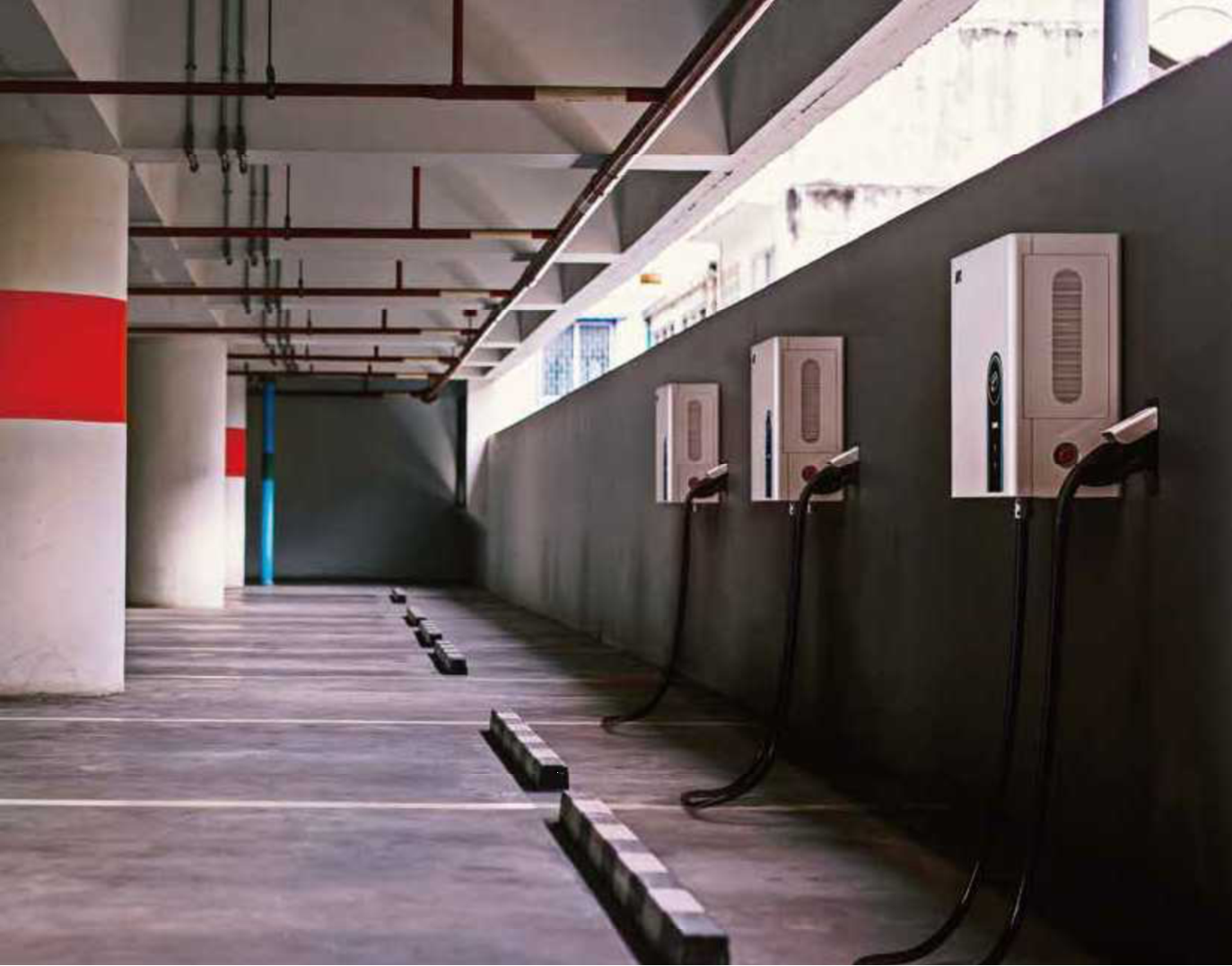
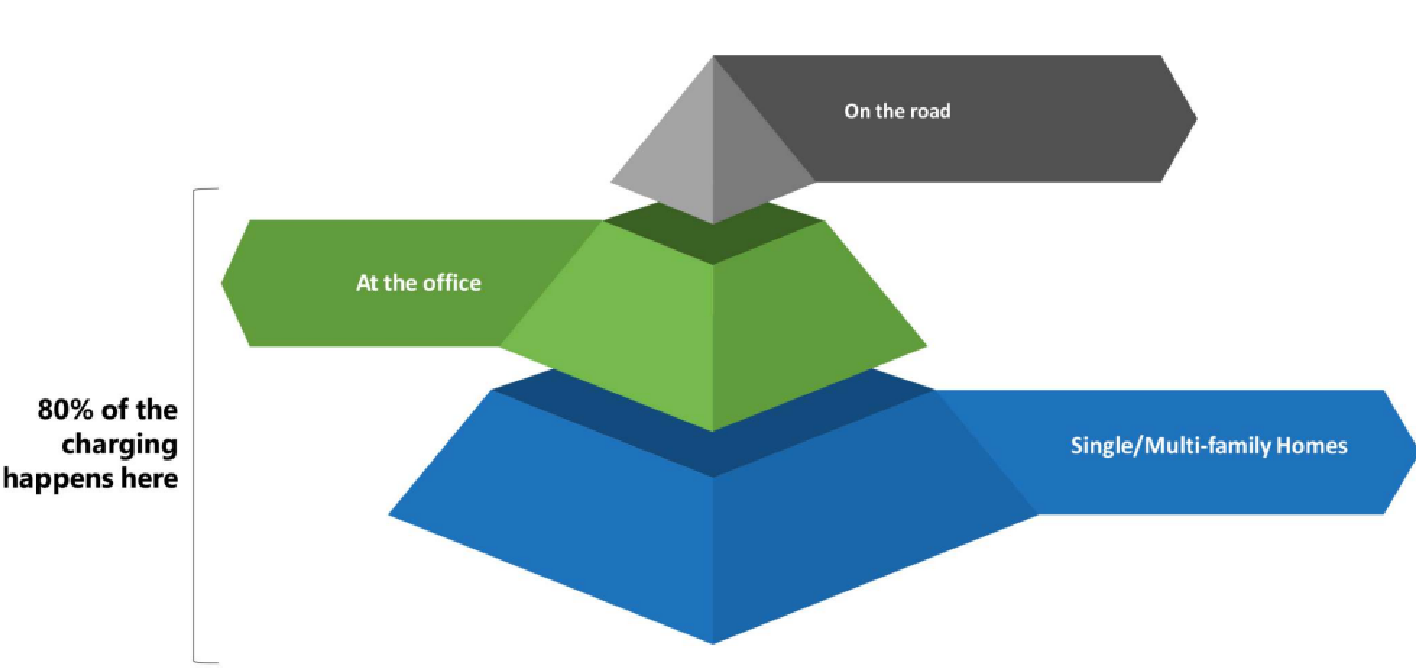
Where do people currently charge their Evs?
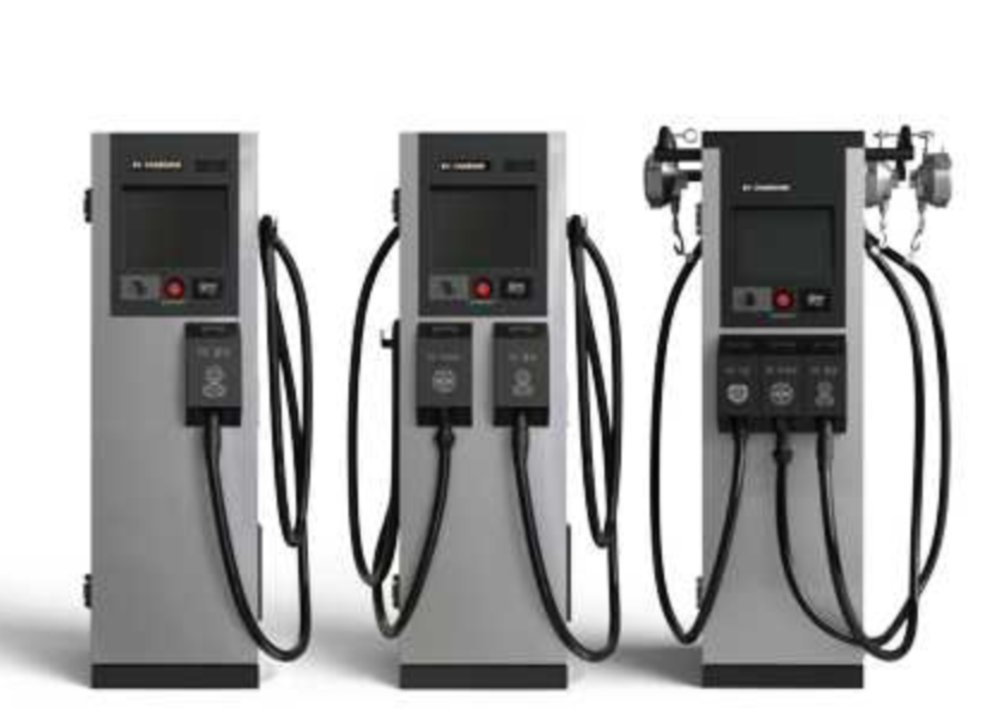
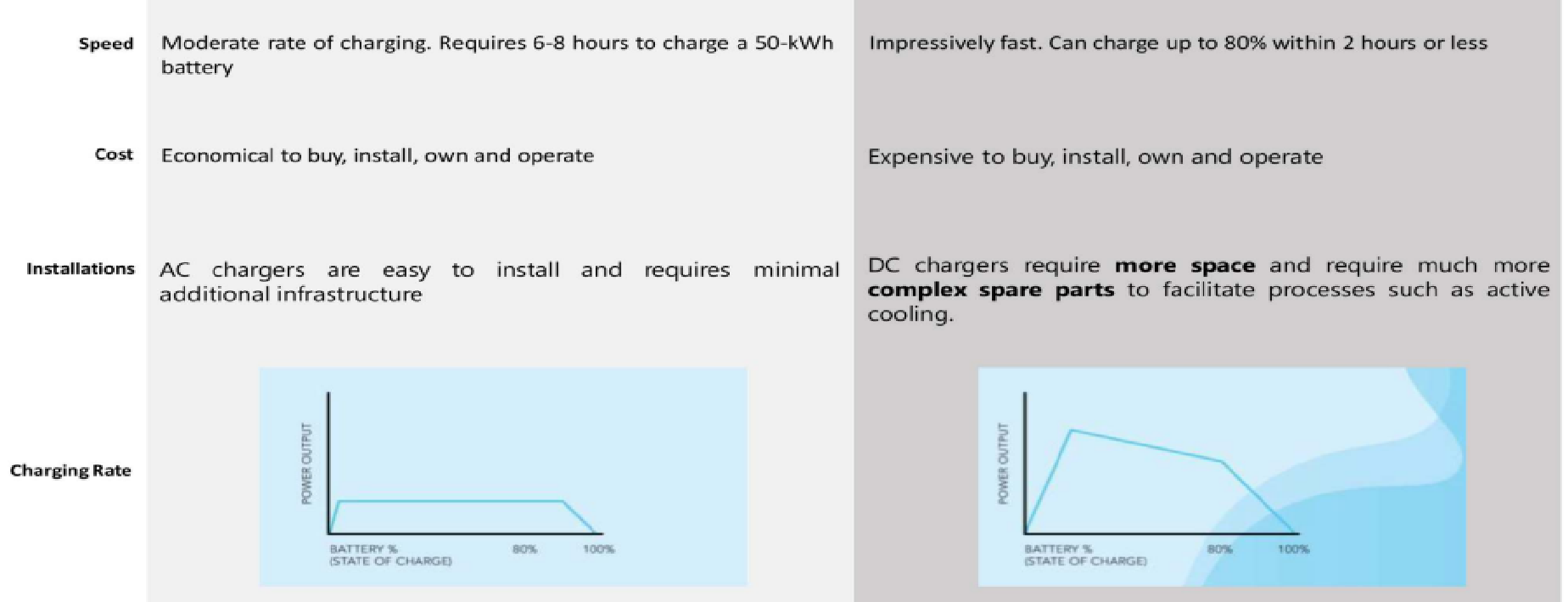
AC Charging vs DC Charging
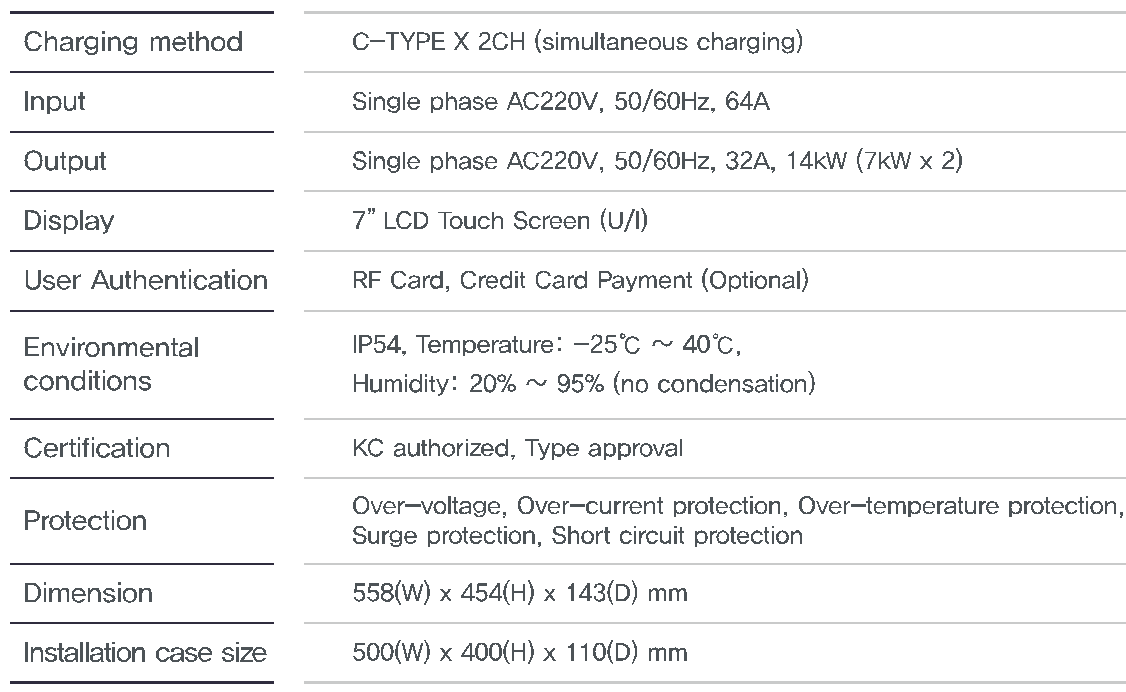
AC Charger
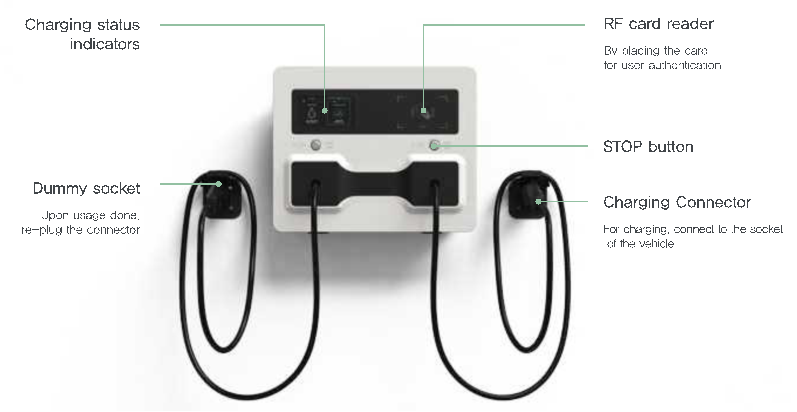

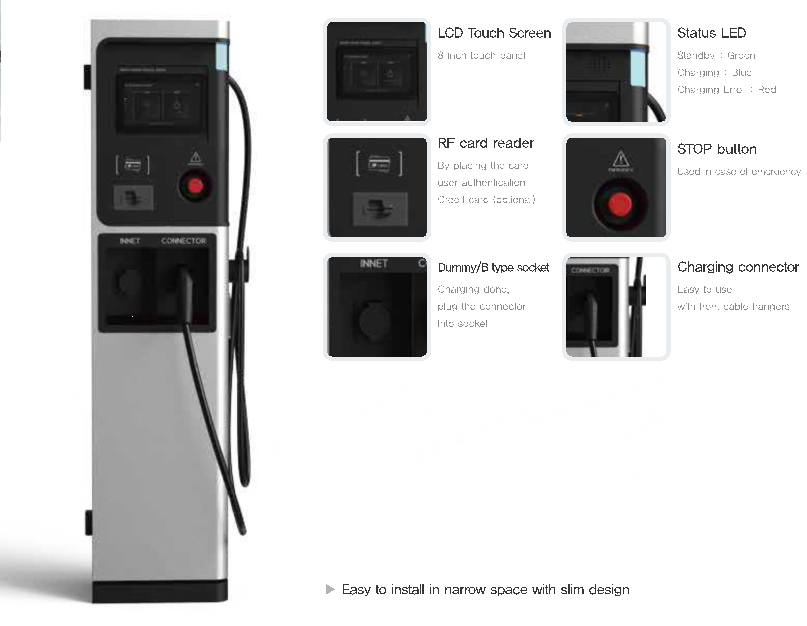
Public AC Charger

DC Charger